The human body is a remarkable system that can heal itself from various injuries and illnesses. However, some body parts are more resilient and faster at healing than others. Here are the top 10 fastest healing body parts, based on their ability to regenerate cells and tissues, and their blood supply.
10. Liver
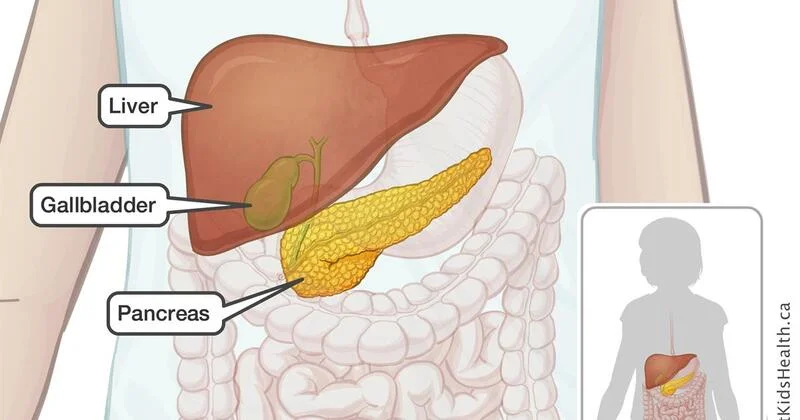
The liver is the largest internal organ in the body, and it performs many vital functions, such as detoxifying the blood, producing bile, and regulating metabolism. The liver is also one of the most regenerative organs in the body, as it can grow back to its original size and function even after losing up to 75% of its tissue. This is because the liver cells, called hepatocytes, can divide and multiply rapidly when needed. The liver can heal itself in about two to four weeks, depending on the extent of the damage.
9. Cartilage
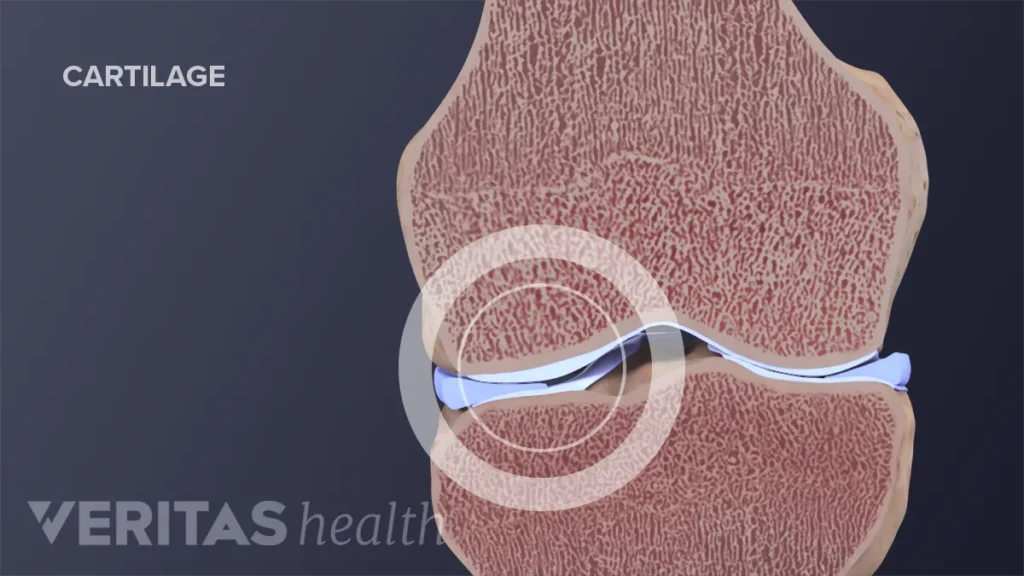
Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that provides cushioning and support to the joints, such as the knees, hips, and elbows. Cartilage has a poor blood supply, which makes it prone to wear and tear over time. However, cartilage also has a high water content, which helps it absorb shock and resist compression. Cartilage can heal itself by producing new cells called chondrocytes, which secrete a matrix of collagen and proteoglycans that form the cartilage structure. Cartilage can heal itself in about four to six weeks, depending on the location and severity of the injury.
8. Ligaments
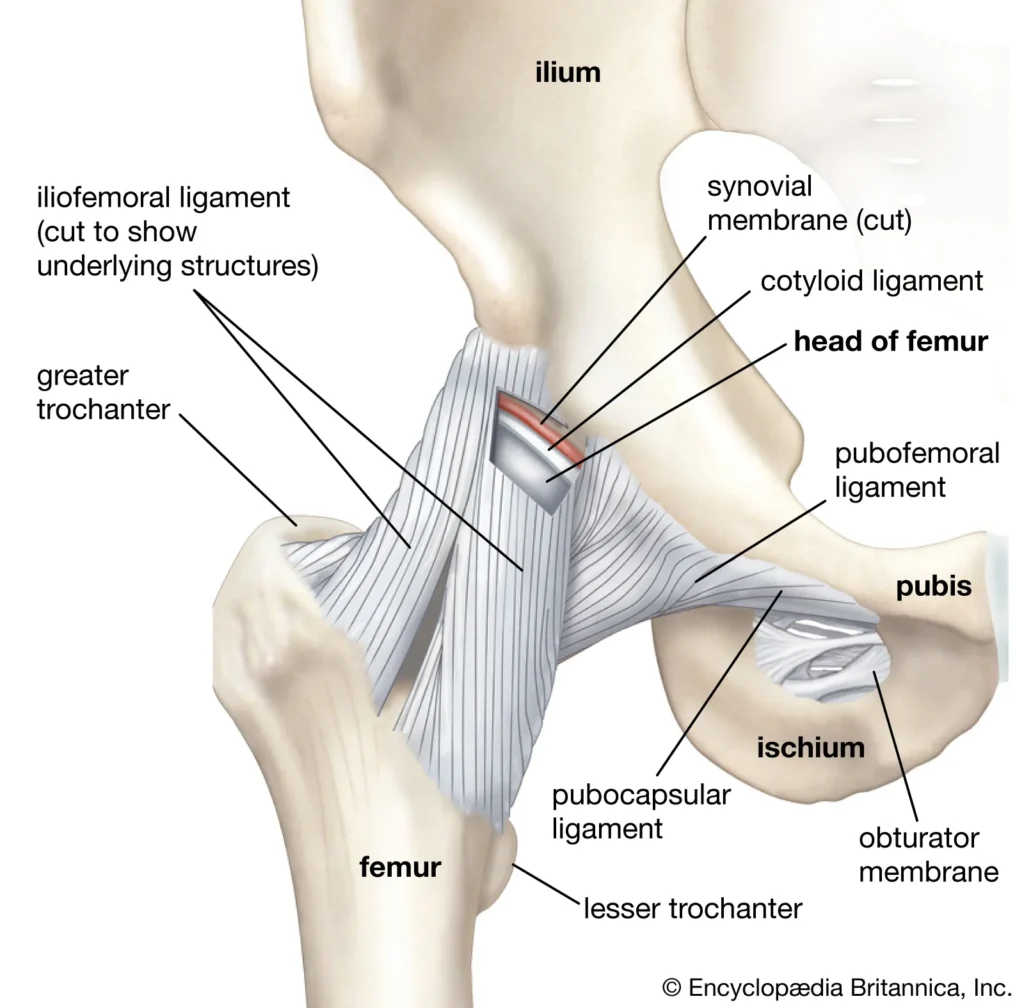
Ligaments are bands of fibrous tissue that connect bones to each other and stabilize the joints. Ligaments are composed of collagen and elastin fibers, which give them strength and flexibility. Ligaments can heal themselves by producing new collagen fibers that bridge the gap between the torn ends. However, ligaments have a limited blood supply, which slows down the healing process and reduces the quality of the repair. Ligaments can heal themselves in about six to eight weeks, depending on the type and location of the injury.
7. Tendons
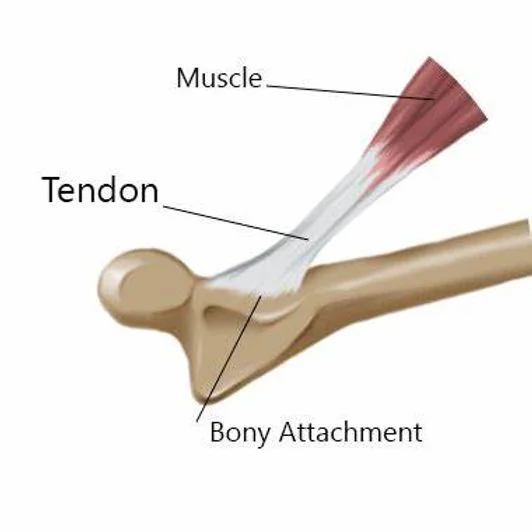
Tendons are cords of fibrous tissue that connect muscles to bones and transmit the force of muscle contraction to the skeleton. Tendons are made of collagen fibers that are arranged in parallel bundles, which give them tensile strength and elasticity. Tendons can heal themselves by producing new collagen fibers that align with the direction of stress. However, tendons also have a poor blood supply, which hampers the healing process and increases the risk of scar tissue formation. Tendons can heal themselves in about eight to 12 weeks, depending on the type and location of the injury.
6. Muscles
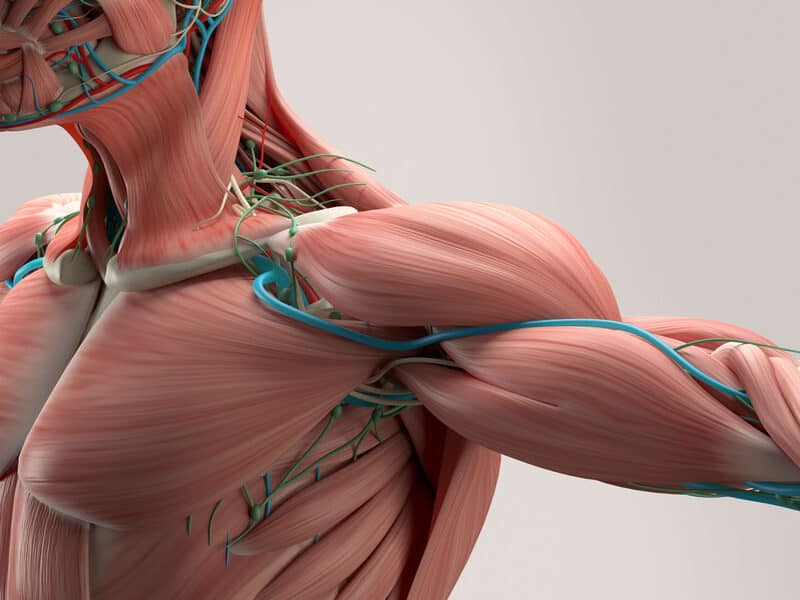
Muscles are groups of specialized cells that contract and relax to produce movement and maintain posture. Muscles are composed of protein fibers called myofibrils, which are surrounded by a network of blood vessels and nerves. Muscles can heal themselves by activating stem cells called satellite cells, which fuse with damaged muscle fibers and regenerate new ones. Muscles have a good blood supply, which facilitates the healing process and delivers oxygen and nutrients to the injured site. Muscles can heal themselves in about two to four weeks, depending on the type and extent of the injury.
5. Skin
Skin is the largest organ in the body, and it covers and protects the underlying tissues from external threats, such as infections, injuries, and ultraviolet radiation. Skin is composed of three layers: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. Skin can heal itself by producing new cells called keratinocytes, which migrate from the edges of the wound to close it. Skin also produces new blood vessels and collagen fibers to restore its structure and function. The skin has a rich blood supply, which accelerates the healing process and prevents infection. Skin can heal itself in about one to three weeks, depending on the size and depth of the wound.
4. Face
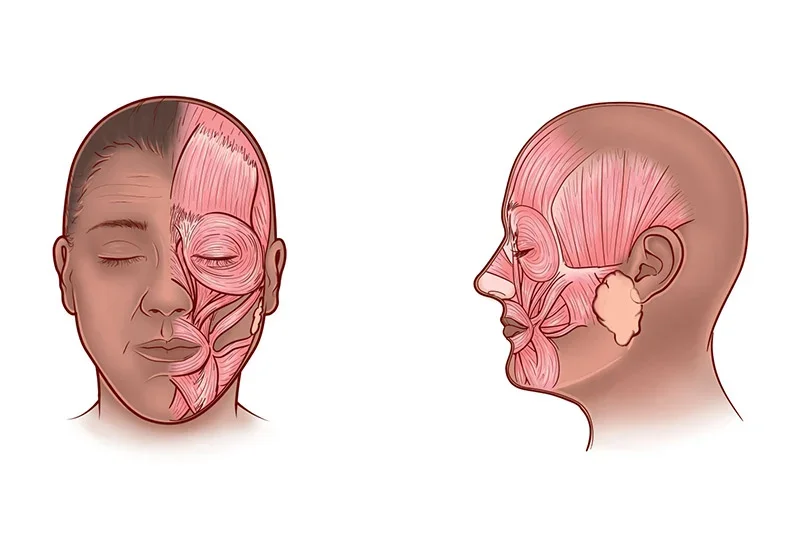
The face is one of the most visible parts of the body, and it plays an important role in communication, expression, and identity. The face is composed of various structures, such as bones, muscles, nerves, glands, and skin. The face can heal itself by activating various mechanisms that promote cell proliferation, migration, differentiation, and remodeling. The face has an abundant blood supply, which enhances the healing process and reduces scarring. The face can heal itself in about one to two weeks, depending on the type and location of the injury.
3. Upper torso
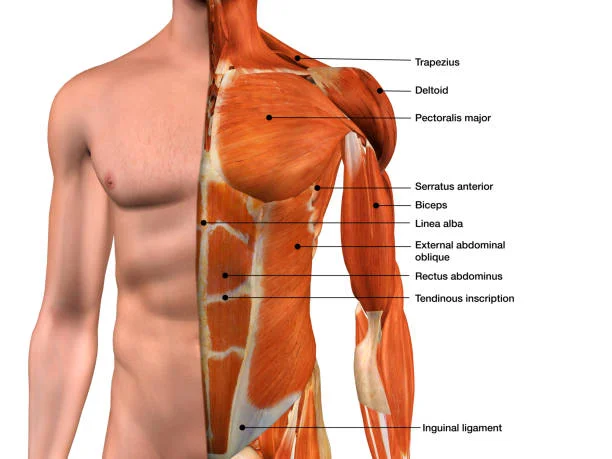
The upper torso is the upper part of the trunk that contains vital organs such as the heart, lungs, liver, spleen, stomach, pancreas, kidneys,
and intestines. The upper torso is protected by a cage of bones called ribs that are connected by muscles and ligaments. The upper torso can heal itself by activating various processes that involve inflammation,
angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), fibroplasia (formation of new connective tissue), and epithelialization (formation of new skin). The upper torso has a moderate blood supply, which supports the healing process and prevents infection. The upper torso can heal itself in about two to six weeks, depending on the type and location of the injury.
2. Fingers

Fingers are the digits of the hand that enable fine motor skills, such as grasping, manipulating, and typing. Fingers are composed of bones called phalanges that are connected by joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles, nerves, and skin. Fingers can heal themselves by activating various factors that stimulate cell growth, migration, differentiation, and maturation. Fingers have a good blood supply, which facilitates the healing process and reduces pain and swelling. Fingers can heal themselves in about two to four weeks, depending on the type and location of the injury.
1. Mouth and tongue

The mouth and tongue are parts of the oral cavity that are involved in chewing, swallowing, tasting, speaking, and breathing. The mouth and tongue are composed of various structures, such as teeth, gums, salivary glands, taste buds, and muscles. The mouth and tongue can heal themselves by producing new cells called epithelial cells, which replace the damaged ones. The mouth and tongue have an excellent blood supply, which speeds up the healing process and prevents infection. The mouth and tongue can heal themselves in about one to two weeks, depending on the type and location of the injury.