The history of human culture has seen countless empires rise and fall.
Many of these empires had a regional or worldwide influence on history. Still, it could be said that some kingdoms were “greater” than others.
However, the ‘greatness’ of an empire is not an easily quantifiable aspect, as several factors are to be considered.
An empire must have political and military control over various communities with diverse cultures and ethnicity to quantify the territory.
In that case here are the top 10 largest empires in history by area:
10. Portuguese Empire
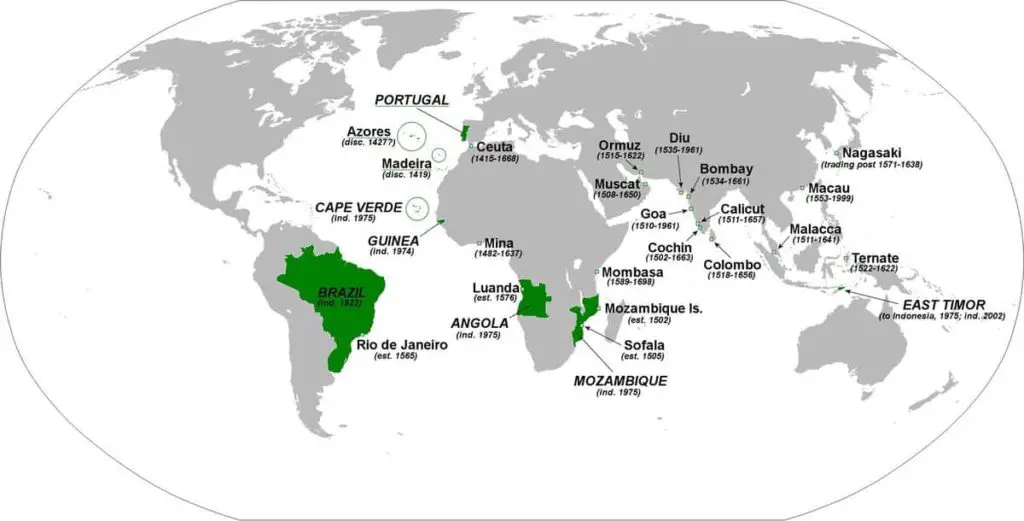
The Portuguese Empire was the earliest and longest-lived colonial empire in European History.
The period ranges from the capture of Ceuta in 1415 to the return of Macau to China in 1999 (almost six centuries).
Portuguese explorers began exploring the African coast in 1419 by taking advantage of the latest developments in shipping, navigation, and maritime technology in search of profitable spice routes.
In 1488, Bartolomeu Dias reached the African coast of the Cape of Good Hope, and in 1498, Vasco da Gama reached Goa, India.
At its height in the year 1815, the Portuguese Empire covered regions known today as Brazil, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe, as well as other areas of Africa that extended across staggering four million square miles.
9. Yuan dynasty
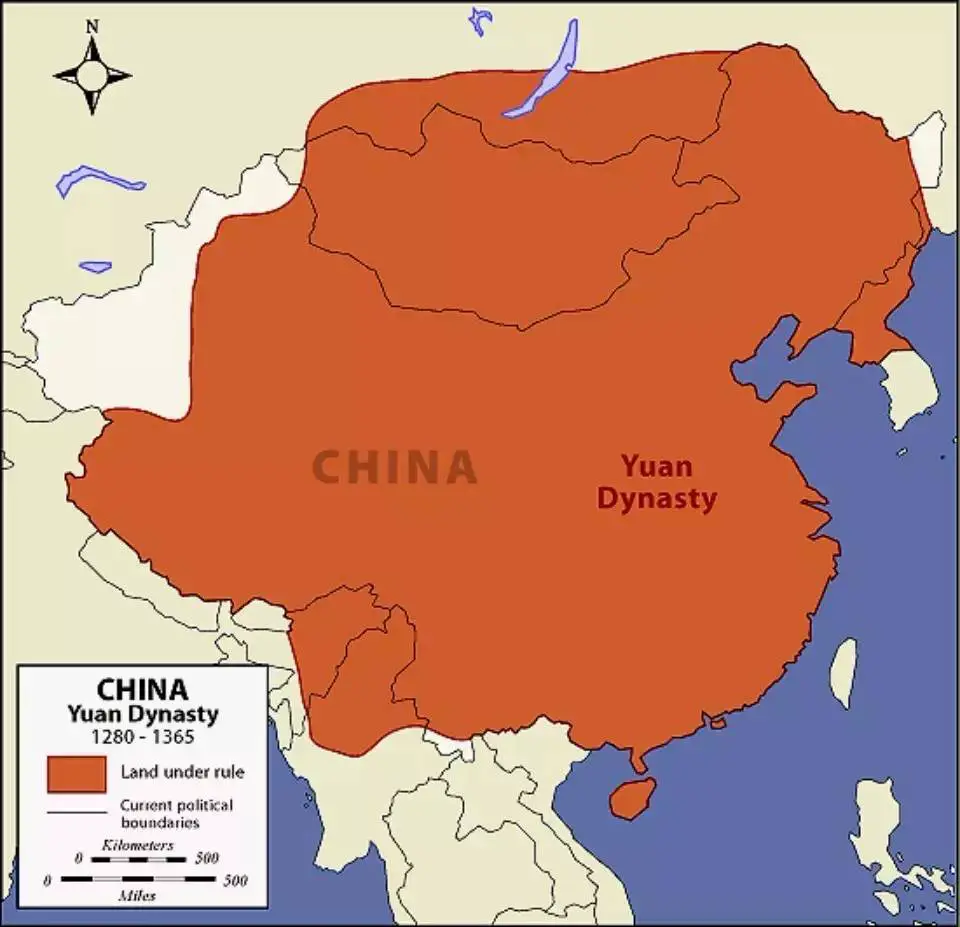
The Yuan Dynasty emerged following the division of the Mongol Empire among the sons of Genghis Khan.
Kublai Khan, a leader of the Mongolian Borjigin clan, received a substantial portion of land, which he transformed into a new ruling dynasty in China.
While the Mongols had already ruled over territories, including northern China, for several decades, it was only in 1271 that Kublai Khan officially established the Yuan Dynasty in the traditional Chinese manner
Kublai and his successors promoted international trade, fostering stability, peace, and economic prosperity within China. The United country opened its doors to the wider world under the Yuan Dynasty’s rule.
8. Umayyad Caliphate
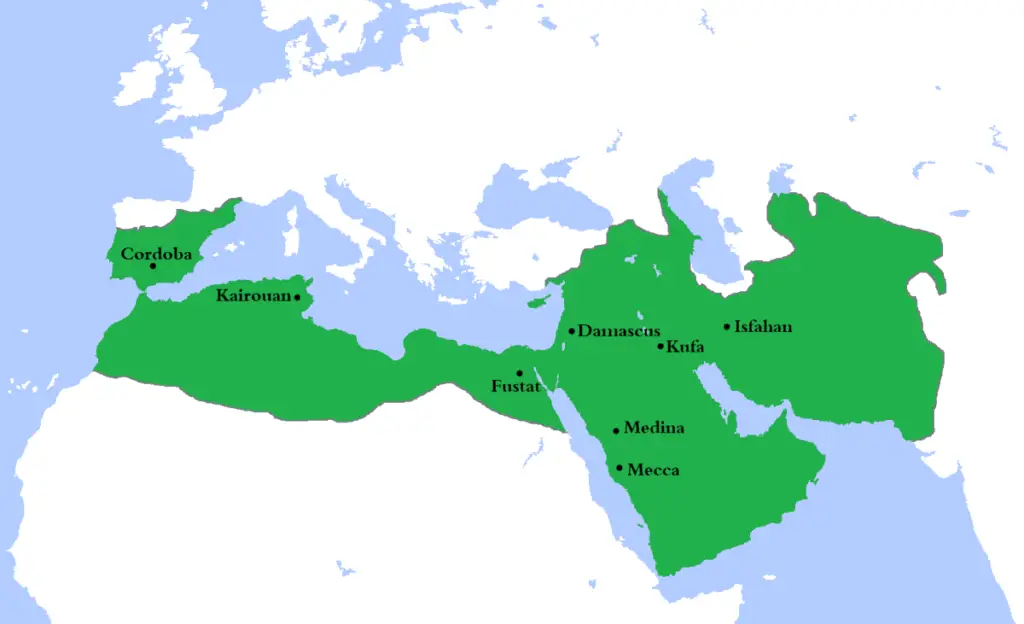
Muawiya, who served as governor of Syria under the Caliphate of Rashidun after the death of the fourth Caliphate, Ali, in 661 CE, founded the dynasty of Umayyad Dynasty.
It was the first dynasty to get the title of the caliphate.
The Umayyads effectively and firmly ruled over the political authority of the caliphate, swiftly crushing rebellions and showing no mercy to instigators or uprisings.
Under the stable authority, Arabic Culture flourished, and the period is often considered the formative period in Arabic art.
7. Abbasid Caliphate
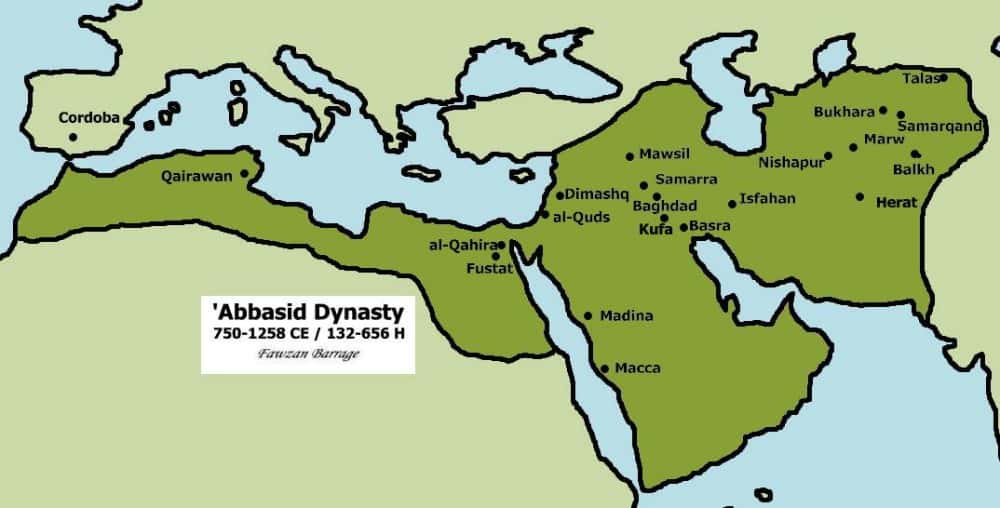
The Abbasid Caliphate, which reigned between 750 and 1258 A.D., held dominion over most of the Muslim world.
It overthrew the Umayyad Caliphate, consolidating power across Umayyad Caliphate holdings, excluding the westernmost limits.
With substantial help from Persia, they defeated the Ummayads and decided to de-emphasize ethnic Arabs by re-establishing a multi-ethnic entity in the Caliphate.
The control of power and the focal point of cultural life in the Islamic middle east shifted eastward from Syria to Iraq.
In 762, Baghdad, the circular city of Peace, was founded to the east as the new capital and was the center of the Caliphate’s political and cultural life.
6. Second French Empire
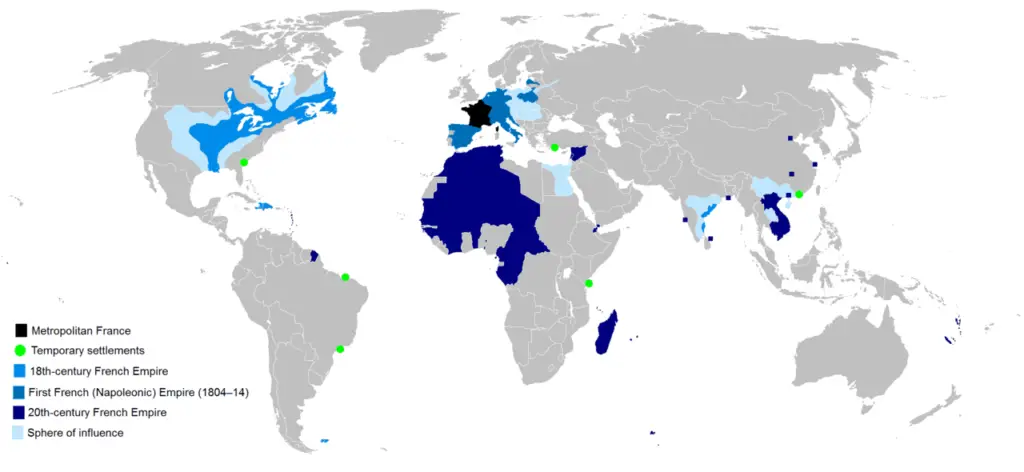
Napoléon III’s regime, from 1852 to 1870, between the Second Republic and the Third Republic in France, is termed the Second French Empire (formally the French Empire).
Although the government machinery of the Second Empire closely resembled that of the First, it operated on different founding/governing principles.
At its height, the Second French Colonial Empire, in 1936, ranked as the second-largest empire globally, covering approximately 10 percent of the Earth’s land area.
The empire extended over 13,500,000 square kilometers (5,200,000 square miles).
5. Qing dynasty
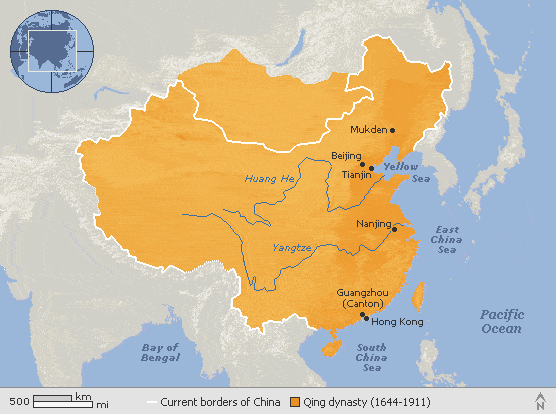
The Qing Dynasty, officially known as the Great Qing, was the final imperial dynasty in China.
It commenced in 1636 and governed China in its entirety from 1644 to 1912.
Preceding the Ming Dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China, the Qing Dynasty tightened imperial Chinese influence over the nation, leaving an indelible mark on Chinese culture.
The reigns of Emperor Yongzheng (1723-1735) and his son Emperor Qianlong (1735-1796) represented the pinnacle of Qing power.
During this period, the Qing Dynasty ruled over a vast territory spanning more than 13 million square miles.
It preceded the Ming dynasty and was succeeded by the Republic of China.
4. Spanish Empire
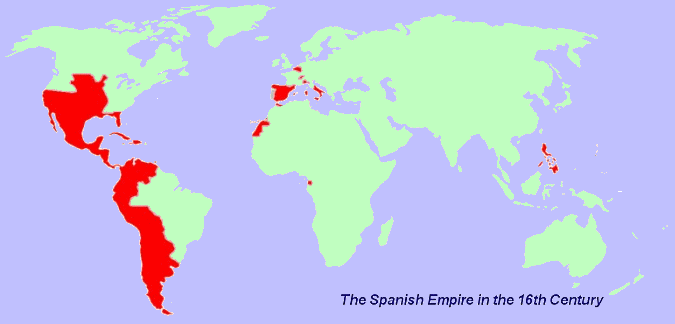
Under the Spanish Crown, the Spanish Empire administered territories and colonies across Europe, the Americas, Africa, Asia, and Oceania.
It was founded in the Age of Exploration and was one of the world’s first global empires.
Spain reached the height of its political and economic strength under the Spanish Habsburgs when its empire became the unstoppable leading global force.
The establishment of the Spanish Empire in the 15th century marked the beginning of the modern global era and European dominance over international affairs in conjunction with the Portuguese Empire.
It stood as the most powerful empire during the 16th and 17th centuries.
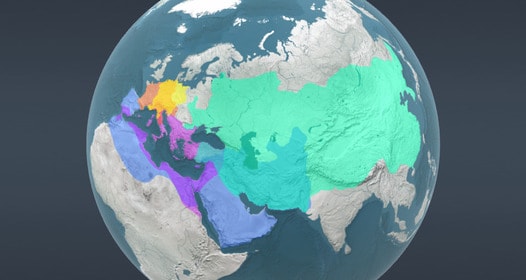
3. Russian Empire
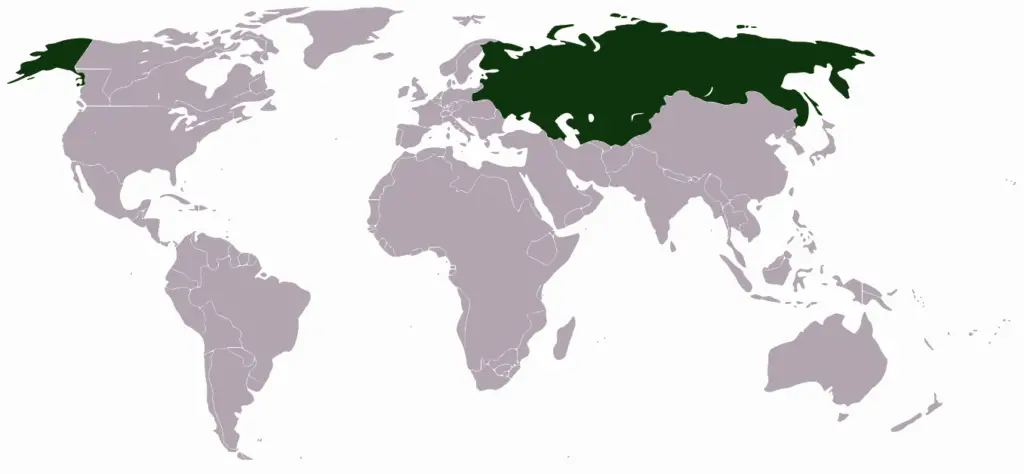
Russian Empire, from 1721 to 1917, extending over the Eastern part of Europe and the continent of Asia, covered almost 14 million square miles (36 million square km).
The Russian Empire ultimately resulted in Russian Muscovite domination over neighboring Europe and Asia, where only the British Empire could rival it in size by the end of the 19th century.
The Russian Empire stretched across the northern portions of Europe and Asia at its peak.
The overall area under the monarch comprised almost one-sixth of the earth’s territory.
It occupied modern-day Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Moldova, Finland, the Caucasus (Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia), significant parts of Poland and Turkey, the Baltic states (Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia), and Central Asian countries (Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan).
2. Mongol Empire
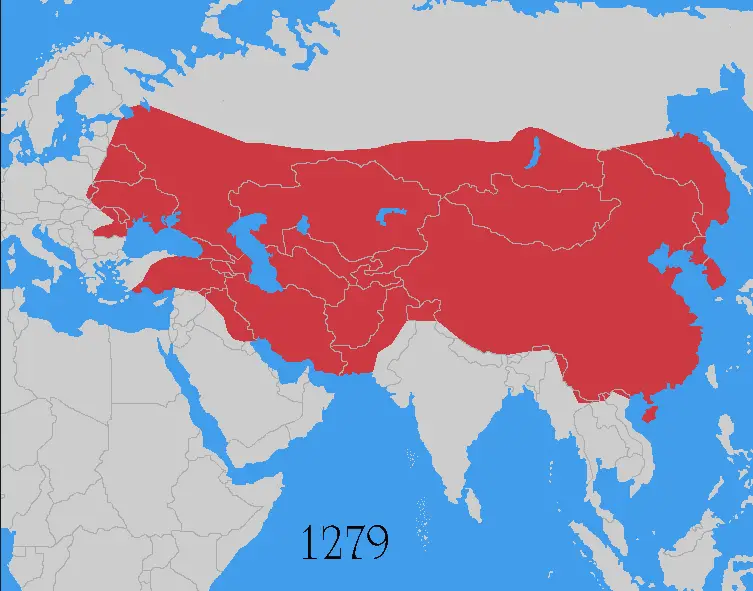
Reaching its peak, the Mongol Empire encompassed the most extensive contiguous land area in history.
Under the leadership of Genghis Khan from 1206 to 1368, the empire expanded across most of Eurasia, leveraging advanced Mongol technology and an immense horde of nomadic warriors.
The loyal warriors of Genghis Khan were rewarded for their loyalty, forging the most successful army of their time.
The Mongol Empire continued to expand rapidly after the death of Genghis Khan in 1227.
His third son, Ögedei Khan, led the empire to new heights, conquering Eastern Europe, Persia, and parts of Central Asia.
Ögedei’s successors, Güyük Khan and Möngke Khan continued the expansion, conquering much of China and reaching as far as Baghdad.
However, the empire began to fracture after the death of Möngke Khan in 1259.
His three brothers fought a civil war for control of the empire, which weakened the Mongol position.
The empire eventually split into four khanates: the Golden Horde, the Ilkhanate, the Chagatai Khanate, and the Yuan Dynasty.
1. British Empire
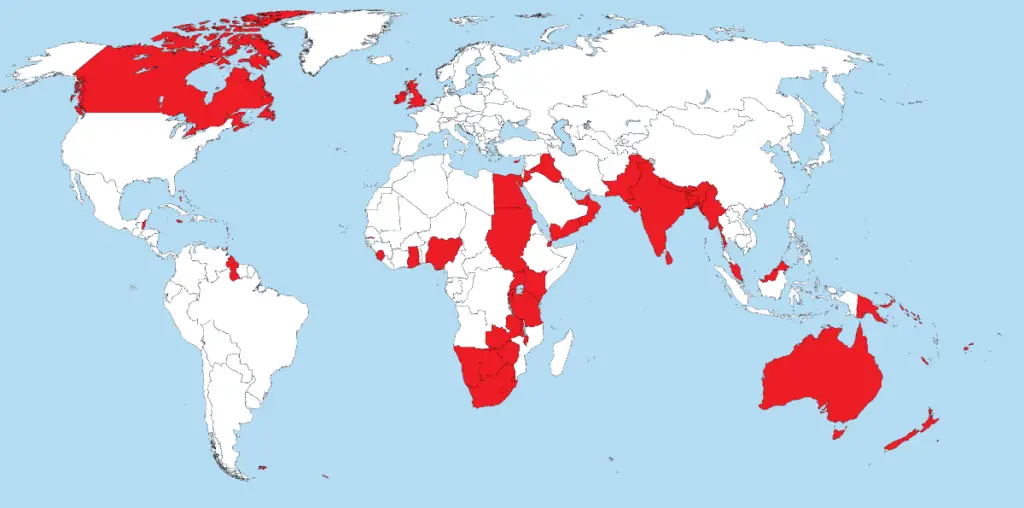
During the 19th and early 20th centuries, the British Empire dominated vast regions across the globe, earning the famous saying: “The sun never sets on the British Empire.”
Comprising the United Kingdom’s dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories, it covered 35.5 million square kilometers, representing 23.84% of the Earth’s surface area.
Surprisingly, the British Empire was nearly twice the size of Pluto’s surface area (17.8 million square kilometers).
The British Empire started with conquering colonies and trading posts abroad and ultimately included dominions, overseas territories, and mandates.
The empire reached its height of global political power when Queen Victoria was proclaimed Empress of India in 1877.
Britain’s relative strength peaked, and Queen’s influence on the Berlin Congress was at its peak.
By 1922, the British Empire had a population of about 458 million, one-fifth of the world population at that time and nearly a quarter of the total earth’s land area.
The history books showcase a remarkable lineup of the top 10 largest empires to ever grace the world.
From the expansive British Empire to the mighty Mongol Empire, these imperial powers left an indelible mark on global history, shaping cultures, economies, and territories on a massive scale.
Examining their areas of influence and heights of power provides valuable insights into the grandeur and reach of these formidable empires.