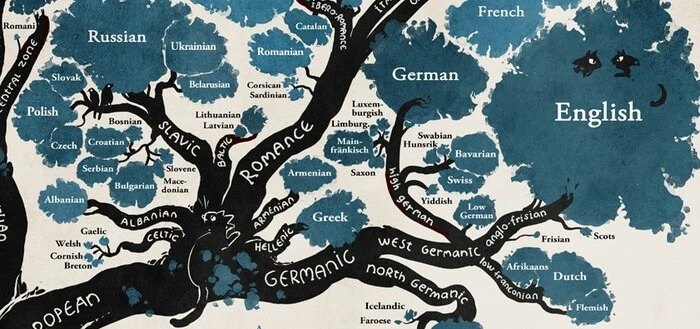
10. Lithuanian

Lithuanian belongs to the Indo-European language family, which gave rise to modern languages such as German, Italian, and English. Lithuanian is closely connected to Sanskrit, Latin, and Ancient Greek, and has far better preserved ancient sounds and grammar rules than any of its linguistic kin. As a result, it is regarded as one of the world’s oldest languages. Today, Lithuanian is the official language of the Republic of Lithuania, as well as one of the European Union’s official languages. Special organizations and linguistic laws safeguard it.
9. Arabic

Arabic is a sacred language since it predates Islam to a very large extent. Arabic is the mother tongue of many languages, including Urdu and Malay. Sugar, algebra, alcohol, and emir are examples of English words with Arabic roots. The first Arabic inscription comes from the year 512 CE. In the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Lebanon, Syria, Iraq, Iran, Israel, Egypt, Jordan, Kuwait, and Oman, around 290 million people use Arabic as their first language.
8. Persian

The Parsa people controlled Iran between 550 and 330 BCE, and their language was Parsi or Persian. It is part of the Indo-Iranian language family, according to experts. It became the Persian Empire’s official language and was spoken throughout the ancient world, from India’s borders in the east to Russia’s in the north, the Persian Gulf’s southern coasts to Egypt, and the Mediterranean in the west. Parsi has evolved into its contemporary form over the years, and Persian is now spoken mostly in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and parts of Uzbekistan.
7. Basque

Basque is a minority language spoken by a small group of people in Spain and France. It has nothing to do with French or Spanish, or any other language on the planet. Linguists have pondered the origins of this cryptic language for centuries, but none of the explanations have been able to stand up to scrutiny. There is one thing that is certain that Basque was spoken in Europe long before Romance languages arrived, and it has endured through the ages in remote corners of the continent.
6. Chinese

The most widely spoken language on the planet is Chinese. It is spoken in China and a few East Asian nations. The Chinese language is a group of languages and dialects that belong to the Chinese-Tibetan language family. The standardized Chinese language is known as “mandarin.” This language had been around for 1200 years before Jesus arrived. Approximately 1.2 billion people speak Chinese now. There are numerous dialects of the language. The hieroglyphs date from the 16th to 11th centuries BC, during the Shang Dynasty. However, in 1956, the written form was streamlined to make it easier to grasp.
5. Greek

Greek is still spoken by about 13 million people and is best recognized as the language of philosophers and scholars. The language is thought to have begun around 1500 BC and is now recognized by the European Union as an official language. Greece and Asia Minor, which is now part of Turkey, were the first places where Greek was spoken.
4. Latin

Latin is one of the most ancient classical languages that has endured the test of time. Latin, like Sanskrit, has influenced a wide range of languages over time. This is where French, Italian, Spanish, Romanian, Portuguese, and today’s most frequently spoken language, English, come from. The beginnings of this language can be traced back to the Roman Empire, which was created around 75 BC. Latin is still the official language of Poland and the Vatican City, and it is studied by millions of people around the world.
3. Hebrew

Many people believe that Hebrew has been around for 5000 years, however, the first written evidence dates from around 1000 BC. It’s also a fascinating case because it died out as a spoken language between 200 and 400 CE, and was only reborn as a living language after the establishment of the state of Israel during WWII. Around 9 million people speak Hebrew around the world now. It has been restored as Israel’s official language after the Israeli people declared it extinct. The Jewish people regard it as a “holy language,” and the Old Testament of the Bible was written in it. Hebrew studies are growing more popular at Western universities.
2. Tamil

Tamil is the official language of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and it is one of the world’s oldest languages, spoken by 78 million people. It is the only old language that has made it into the present world. Tamil is one of India’s official languages and the most widely spoken language in the state of Tamil Nadu. It is part of the Dravidian family, which includes other native southern and eastern Indian languages. In Tamil, inscriptions dating back to the third century B.C. have been discovered.
1. Sanskrit

Sanskrit is one of the oldest, if not the oldest, human languages. It signifies “perfected” or “polished.” It is a member of the Indo-European family’s Indo-Aryan branch. The oldest form of Sanskrit is Vedic Sanskrit, which originates from the second millennium BCE. Sanskrit, also known as “the mother of all languages,” is the most widely spoken classical language on the Indian subcontinent and one of the country’s 22 official languages. Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism all use it as their liturgical language. Scholars distinguish between Vedic Sanskrit and its descendent, Classical Sanskrit; yet, these two types are highly similar, except for significant pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary differences. Sanskrit was originally thought to be a refined method of speaking, a symbol of position and education, studied and used by Brahmins, rather than a separate language. It coexisted with Prakrits, spoken vernaculars that later evolved into current Indo-Aryan languages. Long after it was no longer spoken, Sanskrit was adopted as a first language.